Male Prostate Gland Problems
Male prostate gland problems, aka the male P-Spot and G-Spot a blog about the issues that he may have as he ages.
THE MALE PROSTATE GLAND
ISSUES HE MAY HAVE AS HE AGES
The male prostate gland, an integral part of the male reproductive system, is situated just below the bladder and in front of the bowel. It functions primarily to generate fluid that safeguards and enhances sperm viability. In younger men, the prostate resembles the size of a walnut and envelops the initial portion of the urethra, the channel responsible for carrying urine from the bladder to the penis. This gland is encircled by the nerves responsible for regulating erections.
The prostate gland can be subject to four main disorders, often displaying overlapping symptoms such as frequent nighttime urination, abrupt urges to urinate, difficulties initiating urination, a sluggish urine flow with challenges in stopping, uncomfortable urination, painful ejaculation, and traces of blood in the urine or semen. Additional indications encompass a decrease in sexual desire (libido) and reduced erectile capacity.
While many men tend to view such symptoms as a natural consequence of aging, it’s important to recognize that swift medical attention is crucial. Consulting a doctor promptly can lead to early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, potentially circumventing more severe health complications.
.
.
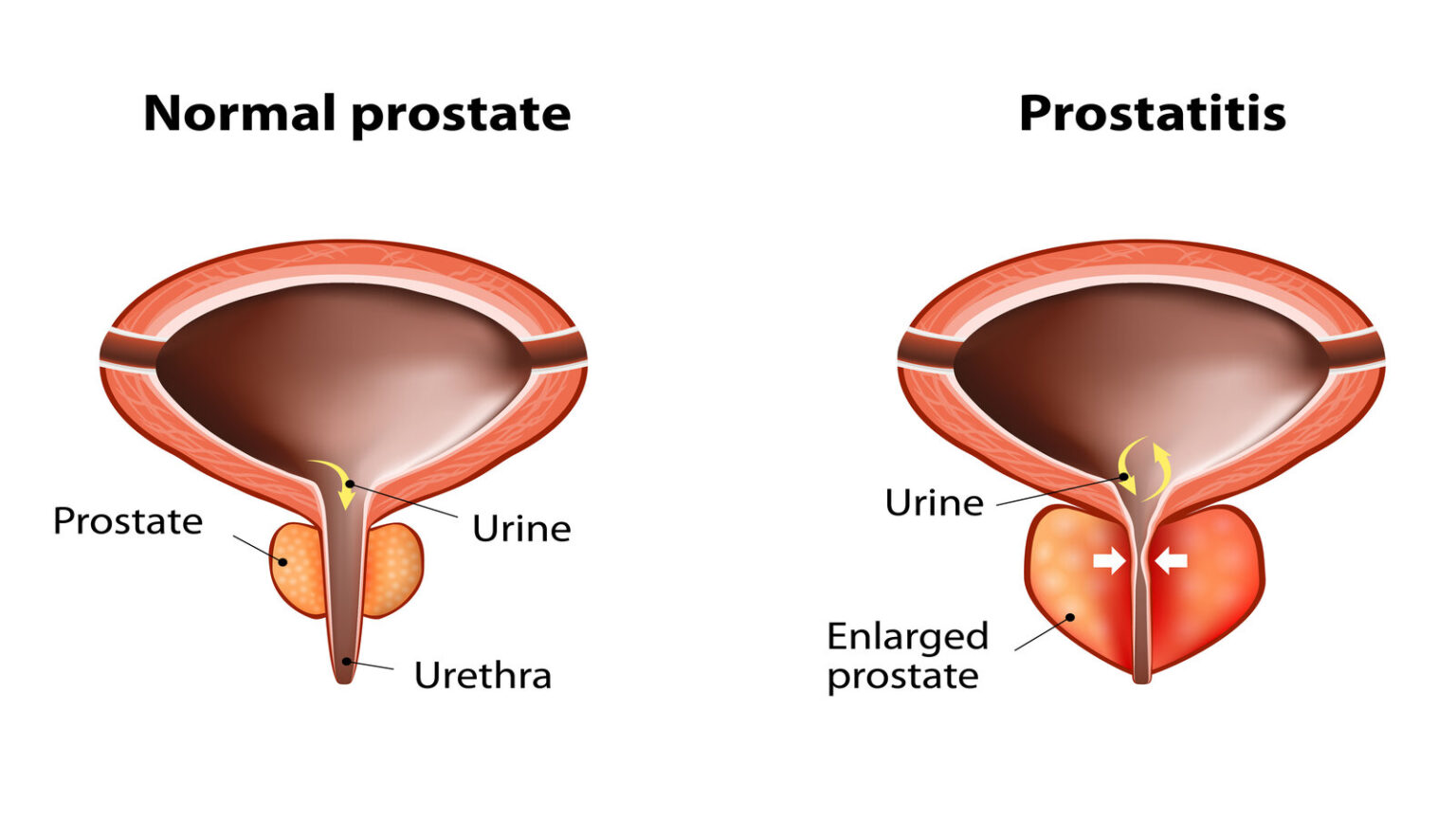
PROSTATITIS
Prostatitis, characterized as a benign condition, stands distinct from prostate cancer, signifying its non-life-threatening nature. The condition emerges due to inflammation, engendering swelling within the prostate. Its manifestations encompass persistent discomfort nestled deep within the pelvic region, which can persist consistently or arise during urination and ejaculation. The intensity of this discomfort can escalate to pain and may even radiate to adjacent pelvic areas. In instances where an infection is the underlying cause, antibiotics may be employed as part of the treatment protocol.
It is pertinent to acknowledge that the approach to treating prostatitis is tailored to the specifics of each case. Variations exist in the types of prostatitis, with some proving to be more challenging to address, particularly if symptoms have endured unaddressed over an extended period. In such scenarios, comprehensive treatment strategies become essential to curtail the persistence and escalation of symptoms.
.
Male Prostate Gland Problems
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF
PROSTATITIS?
Detecting prostatitis in males often involves recognizing a combination of symptoms and seeking medical evaluation for proper diagnosis. Some common indicators that may suggest the presence of prostatitis include:
- Pelvic Discomfort: Persistent or intermittent pain or discomfort in the pelvic region, lower abdomen, or lower back.
- Urinary Symptoms: Changes in urinary habits, such as increased frequency of urination, urgency, difficulty starting or stopping urination, or a weakened or interrupted urine stream.
- Painful Urination: A burning sensation or pain while urinating.
- Painful Ejaculation: Discomfort or pain during or after ejaculation.
- Genital Pain: Pain or discomfort in the genital area, including the penis, testicles, or perineum (the area between the scrotum and anus).
- Flu-Like Symptoms: Some individuals may experience flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, body aches, and fatigue.
- Sexual Dysfunction: Prostatitis can sometimes lead to sexual problems, including erectile dysfunction or decreased sexual desire.
It’s important to note that the severity and combination of symptoms can vary among individuals. If a male notices any persistent or unusual symptoms related to urination, sexual function, or discomfort in the pelvic region, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
A doctor can conduct a physical examination, review medical history, and perform appropriate tests, which may include urine tests, blood tests, and potentially a prostate exam, to determine the presence of prostatitis or other underlying conditions.
.
.
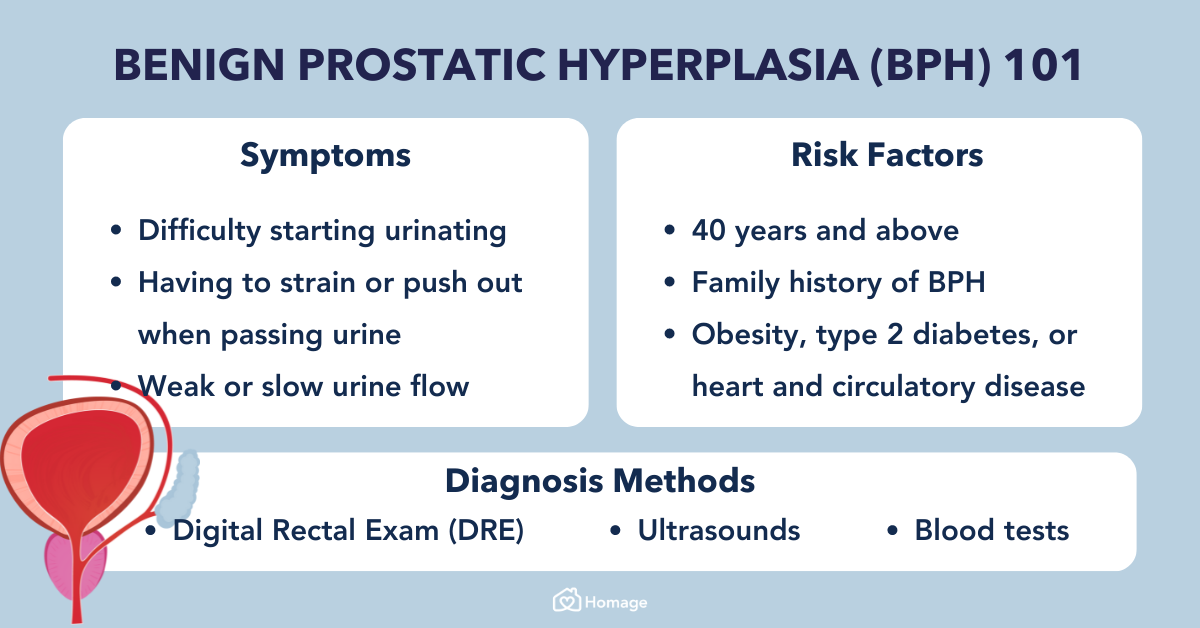
BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA (BPH)
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), also referred to as prostate enlargement (BHE), frequently manifests in older men and is characterized by non-malignant growth. It’s essential to emphasize that BPH is distinct from prostate cancer. As men age, it is quite typical for some degree of prostate enlargement to develop, particularly from the age of 50 onward. However, if the enlargement reaches a point where it constricts the urethra traversing the prostate, it can lead to difficulties in urination.
While BPH is a prevalent occurrence, it is important to note that it is not life-threatening and can be effectively managed. Treatment approaches for BPH can encompass the use of antibiotics, and in more advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to widen the passage of the urethra. This procedure, known as a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), involves the insertion of an instrument through the urethra via the penis, allowing for the removal of a portion of the prostate to enhance urine flow. Typically conducted under general anesthesia, this surgical intervention typically entails a hospital stay of a few days, with the placement of a catheter during the recovery period..
.
.
BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA (BPH) MASSAGE — Holistic Prostate Massage To Relieve Swelling
.
..
PROSTATODYNIA (CPPS)
Prostadynia, also known as chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS), is a complex and often perplexing condition that primarily affects males. This chronic disorder is characterized by persistent pain and discomfort in the pelvic region, particularly within the area surrounding the prostate gland. Unlike acute prostatitis, there are usually no clear indications of infection or inflammation, making diagnosis and management a challenging endeavor.
Individuals grappling with prostadynia often find themselves navigating a perplexing journey, as the exact underlying cause of the condition remains elusive in many cases. Despite the absence of evident infection, the discomfort experienced can be quite distressing, significantly impacting an individual’s quality of life and overall well-being.
The symptoms associated with prostadynia can be diverse, ranging from dull aches to sharp pains in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or genital region. Pain may be intermittent or constant and may vary in intensity. Some individuals also report discomfort during urination or ejaculation, adding to the complexity of the condition.
Managing prostadynia involves a multidimensional approach that takes into consideration the diverse factors that may contribute to the chronic pain and discomfort. Treatment strategies can encompass a combination of approaches, such as:
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or muscle relaxants may be prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Alpha-blockers: These medications are sometimes used to relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, potentially improving urinary symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Pelvic floor physical therapy may be beneficial in relieving tension and enhancing muscle function in the pelvic area.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Dietary changes, stress management techniques, and avoiding potential triggers can play a role in symptom alleviation.
- Counseling and Psychological Support: Chronic pain can have psychological and emotional implications. Counseling and relaxation techniques may help individuals cope with the challenges of prostadynia.
- Trigger Point Injections: In some cases, injections of anesthetic agents or corticosteroids into specific trigger points may provide relief from localized pain.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of treatments may vary from person to person, and a comprehensive and patient-centered approach is crucial in managing prostadynia.
.
Male Prostate Gland Problems
PROSTATE CANCER
Among the four discussed prostate disorders, it is imperative to recognize that Prostate Cancer stands as the sole condition with the potential to pose a life-threatening risk. What adds to the concern is that many instances of prostate cancer develop stealthily, often progressing devoid of any discernible symptoms, thus heightening the challenge of early detection.
Every year, the landscape witnesses approximately 18,700 Australian men grappling with a prostate cancer diagnosis, a figure compounded by over 3,000 succumbing to the disease. This unsettling reality positions prostate cancer as the second leading cause of male cancer-related fatalities, following closely behind lung cancer. Startlingly, the statistics underscore that nearly one in every eleven men will eventually encounter prostate cancer during the course of their lives.
Prostate cancer originates from an abnormal surge in the reproduction of cells within the prostate, a gland forming an integral part of the male reproductive system. This unchecked proliferation gives rise to swelling or the formation of a tumor within the prostate. A distinctive feature that sets prostate cancer apart from the previously discussed benign prostatic hyperplasia is the potential for cancerous cells to break free from the confines of the prostate, infiltrating distant regions of the body, notably the bones and lymph nodes. This metastatic journey results in the emergence of secondary tumors, marking a critical phase in the progression of the disease.
Once prostate cancer cells breach the confines of the prostate and initiate metastasis, the scenario takes on a heightened level of complexity. While treatment avenues remain open, the prospect of a definitive “cure” diminishes considerably. This pivotal juncture underscores the significance of timely detection and intervention, underscoring the critical role that awareness, regular screening, and proactive medical consultation play in the ongoing battle against prostate cancer.
.
.
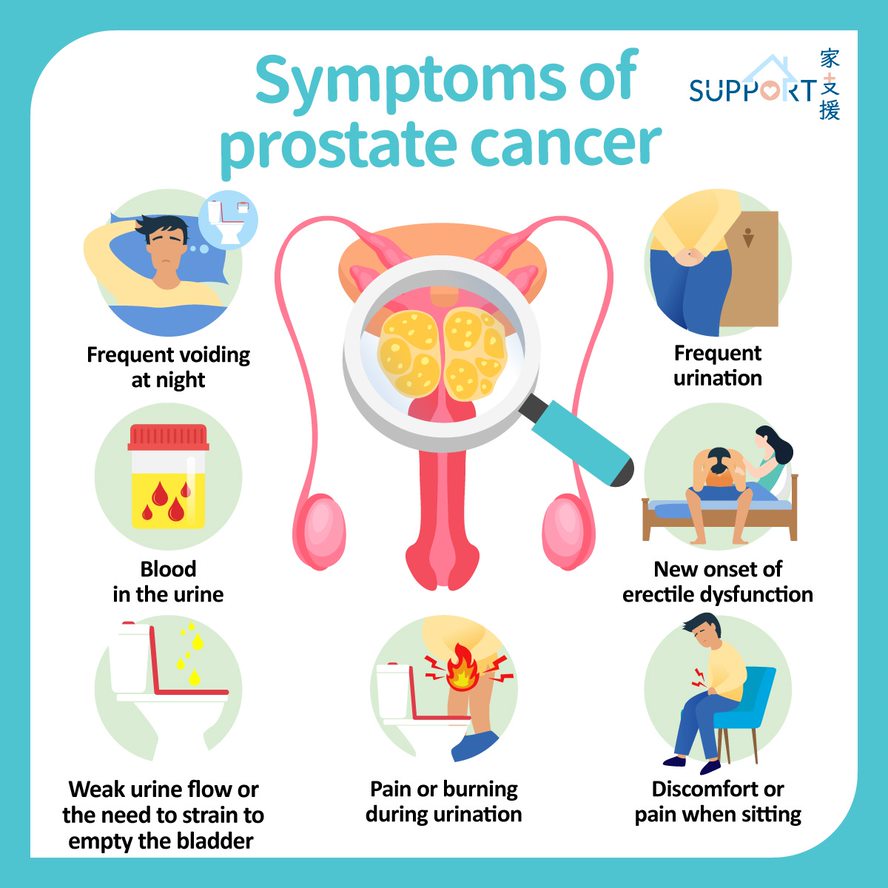
SYMPTOMS OF PROSTATE CANCER
Detecting prostate cancer in its early stages is crucial for effective treatment and improved outcomes. While prostate cancer can develop without causing noticeable symptoms, there are certain signs and indicators that individuals should be vigilant about. Some of the potential signs of prostate cancer include:
- Changes in Urination: An alteration in urinary habits, such as increased frequency of urination, particularly during the night (nocturia), difficulty starting or stopping urination, weakened urine flow, or a sensation of incomplete bladder emptying.
- Blood in Urine or Semen: The presence of blood in urine (hematuria) or semen can be an indicator that warrants medical attention.
- Discomfort or Pain: Pain or aching sensations in the lower back, hips, pelvis, or upper thighs may be indicative of prostate issues.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Difficulty in achieving or maintaining an erection, particularly if it’s a new or persistent concern, should be investigated.
- Painful Ejaculation: Experiencing discomfort or pain during or after ejaculation can be a signal of prostate-related issues.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: A sudden and unexplained drop in weight can be associated with various health concerns, including prostate cancer.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or fatigued, even with adequate rest, may prompt further investigation.
- Changes in Bowel Habits: While less common, some individuals with prostate cancer may experience alterations in bowel habits, such as constipation or changes in stool consistency.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other non-cancerous conditions. Nonetheless, if you notice any persistent or unusual changes in your urinary, sexual, or overall health, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
Regular prostate screenings, including prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests and digital rectal examinations, are essential for early detection and timely intervention. Early diagnosis significantly enhances the likelihood of successful treatment and improved quality of life.
.

.
PROSTATE CANCER IS USUALLY
A SLOW GROWING CANCER
Prostate cancer typically exhibits a slower growth pattern compared to other cancers. Historically, it was predominantly identified in men aged 70 and above, with many succumbing to unrelated causes before the prostate cancer could progress to a lethal stage. This phenomenon coined the adage “most men die with, not of, prostate cancer.” However, the landscape has undergone significant shifts, thanks to three pivotal developments:
- Extended Lifespan: The increasing longevity of men provides prostate cancer with more time to extend beyond the confines of the prostate, potentially leading to dire consequences.
- Shifting Age Distribution: More men in their early sixties, fifties, and even forties are now being diagnosed with prostate cancer. This earlier onset, coupled with the expanding male life expectancy, grants these cancers an extended timeframe to metastasize and evolve into life-threatening conditions unless identified and addressed promptly.
- Aggressive Nature in Younger Men: Prostate cancer diagnosed in younger men often displays a more aggressive nature, accelerating its progression and posing a heightened life-threatening risk within a shorter span.
Initiating appropriate treatment while the cancer remains localized within the prostate gland offers the prospect of “curing” the condition. The potential for cure underscores the paramount importance of early detection.
It is imperative for all men to be cognizant of their susceptibility to the disease and contemplate regular testing starting from the age of 50, or even from the age of 40 if a family history of prostate cancer exists. Embracing proactive screening measures empowers individuals to stay ahead of potential prostate health challenges and underscores the significance of timely intervention in safeguarding overall well-being.
.

Male Prostate Gland Problems
THE PROSTATE CANCER
HOLISTIC APPROACH
Alongside conventional medical treatments, individuals may explore various alternative and complementary approaches to enhance their overall well-being and address prostate cancer. It’s crucial to emphasize that consultation with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the suitability of alternative medical strategies for each individual. Here are several alternative approaches that have garnered attention:
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a healthy and balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins may contribute to overall well-being. Some research suggests that certain dietary choices, such as reducing red meat consumption and incorporating foods high in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, may have potential benefits in managing prostate cancer.
- Herbal Supplements: Some herbal supplements, such as saw palmetto, green tea extract, and pomegranate extract, have been studied for their potential effects on prostate health. However, their efficacy and safety should be thoroughly researched and discussed with a healthcare provider.
- Mind-Body Practices: Mindfulness meditation, yoga, and relaxation techniques can help manage stress, improve mental well-being, and enhance the body’s natural healing processes. These practices may play a supportive role in conjunction with medical treatments.
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese practice involving the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body, is believed by some to help alleviate pain, reduce side effects of treatments, and promote overall wellness.
- Nutritional Supplements: Some individuals opt for nutritional supplements, including vitamins, minerals, and herbal extracts, to potentially bolster their immune system and support their body’s ability to fight cancer. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider before adding supplements to your regimen, as some may interact with medications or have adverse effects.
- Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can have numerous health benefits, including supporting the body’s natural defense mechanisms. Exercise may help improve circulation, boost energy levels, and promote overall well-being.
- Mind-Body Therapies: Therapies such as hypnotherapy, biofeedback, and guided imagery aim to harness the mind’s power to influence physical health and healing processes. While not a substitute for medical treatment, these therapies may contribute to a comprehensive approach to prostate cancer care.
- Massage Therapy: Some individuals find massage therapy to be relaxing and soothing, helping to alleviate stress and promote a sense of well-being. However, it’s important to choose a qualified massage therapist who is experienced in working with cancer patients.
It’s crucial to approach alternative approaches with caution and to involve your healthcare team in the decision-making process. Integrating complementary practices into your prostate cancer management plan should be done under the guidance of qualified healthcare professionals to ensure safety and effectiveness.
.
.
I HOPE YOU ENJOYED TODAY’S BLOG ABOUT MALE PROSTATE HEALTH
I trust you found today’s blog post informative and engaging, as it delved into a comprehensive exploration of the male prostate gland, shedding light on various aspects including prostatitis, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatodynia, and the critical issue of prostate cancer. Recognizing the significance of male sexual health, the article aimed to provide valuable insights into these crucial topics.
.
.
SCAR TISSUE FROM PROSTATE BRACHYTHERAPY CANCER TREATMENT — A 52 Year Old Male’s Story
.
.
.
.
Male Prostate Gland Problems
 Written on August 9th, 2013 by Aleena Aspley, who is a Certified Sexological Bodyworker.
Written on August 9th, 2013 by Aleena Aspley, who is a Certified Sexological Bodyworker.
Aleena is open to seeing people of all genders and sexual orientations. Her Somatic Sexology & Intimacy Coaching NEO Tantric bodywork studio is located in North Brisbane, Queensland Australia.
.
.
MY WEBSITES
Women: YoniWhisperer.com.au
Couples: TantricWhisperer.com
My Bodywork Directory – AleenaAspley.com/
.
.
.
MY CONTACT DETAILS
Ms. Aleena Aspley
Certified Sexological Bodyworker / Somatic Sex Educator
NEO Tantra & Chakrassage Professional
.
.
My Bodywork Studio: North Brisbane, Queensland
Phone: 0404 449 433 (Text me to Book)
Overseas: +61 404 449 433
By Appointment: Monday to Friday until 9pm
I work occassional weekends – just ask
My Bodywork Directory – www.AleenaAspley.com
Male Prostate Gland Problems
.
..
.
.
The Male Prostate Gland
Problems He May Have As He Ages